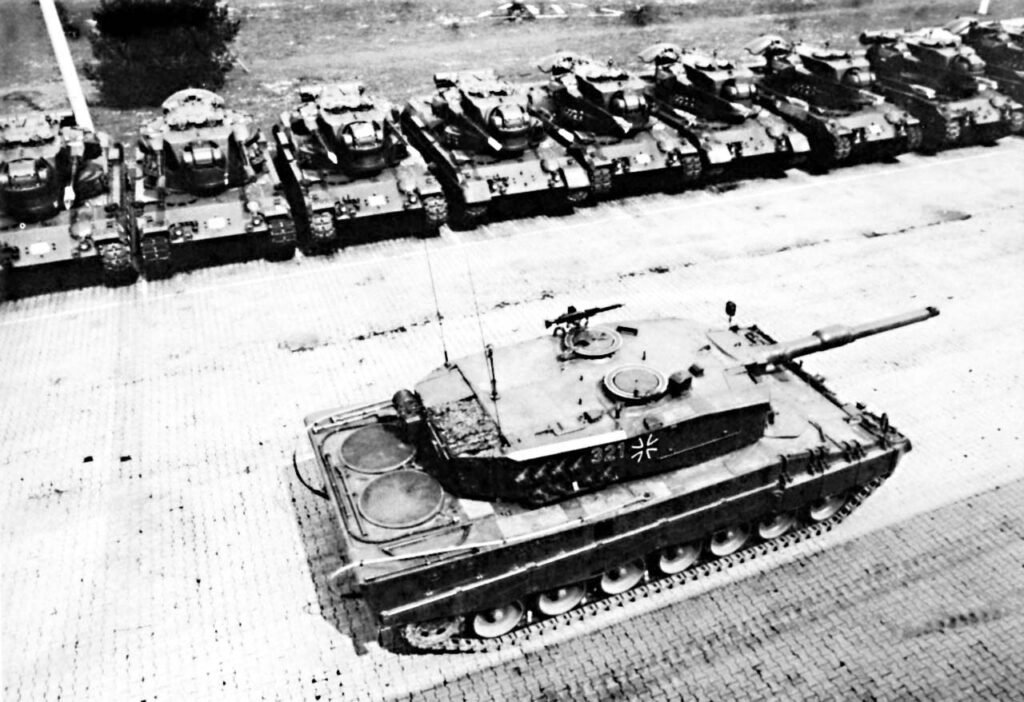
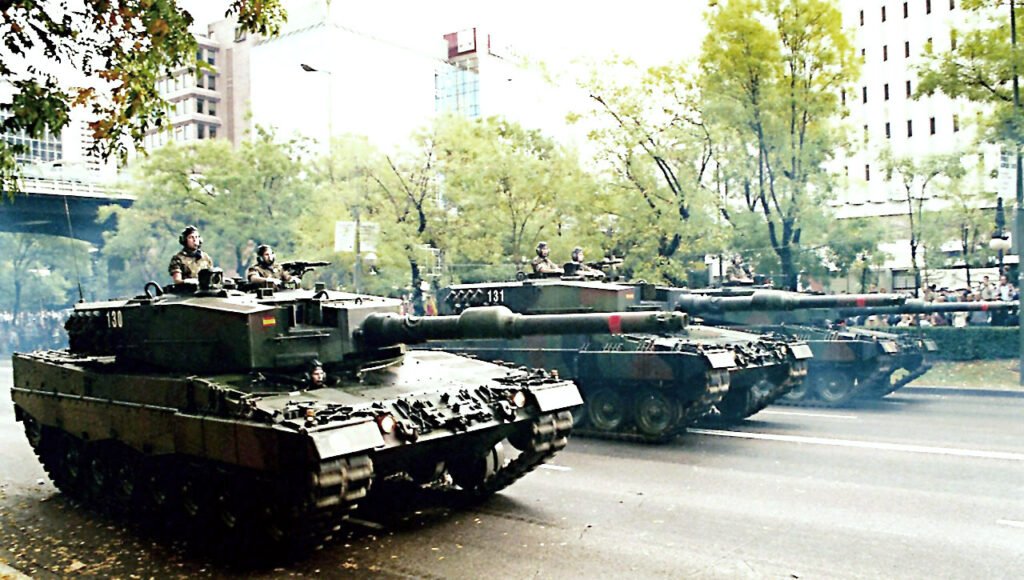
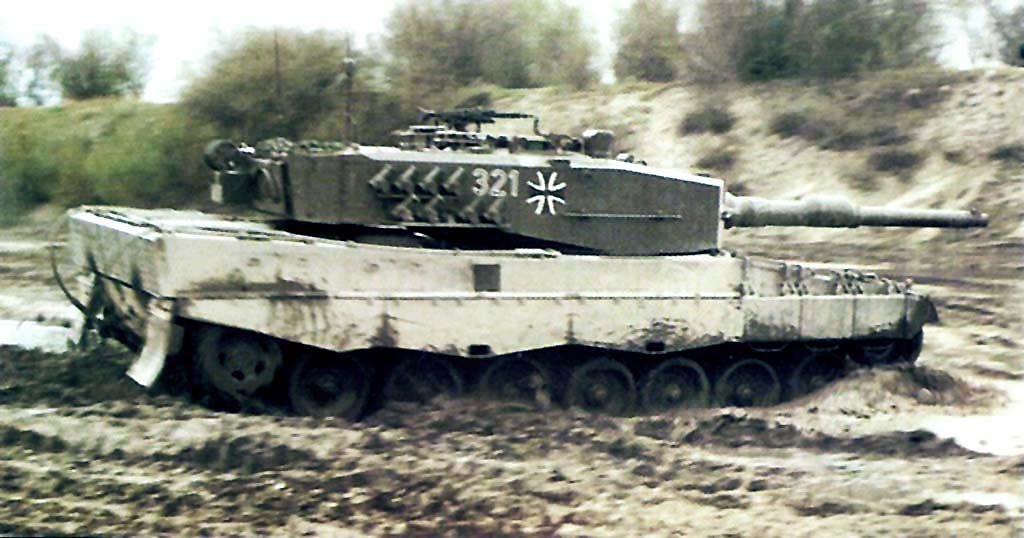
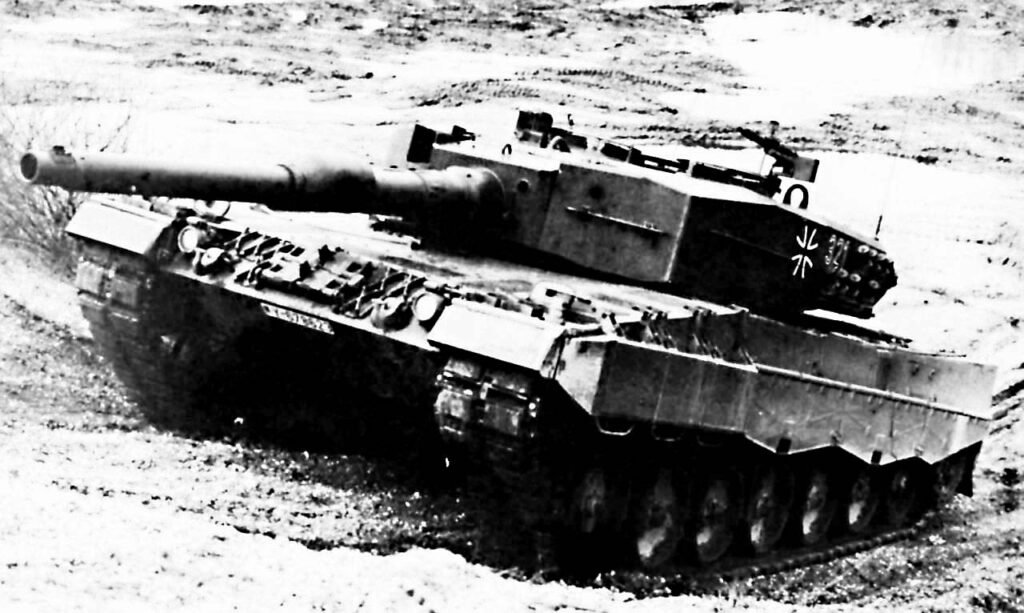
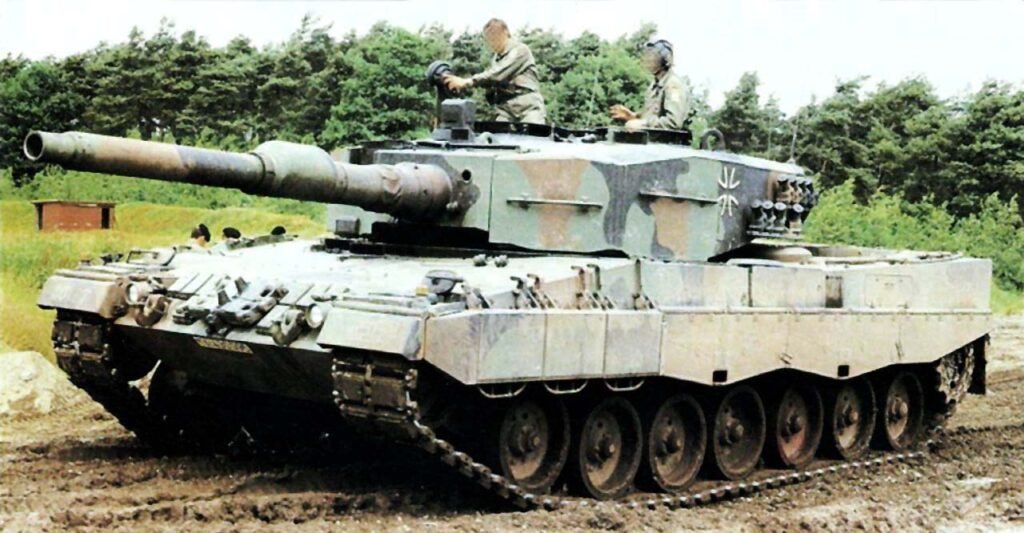
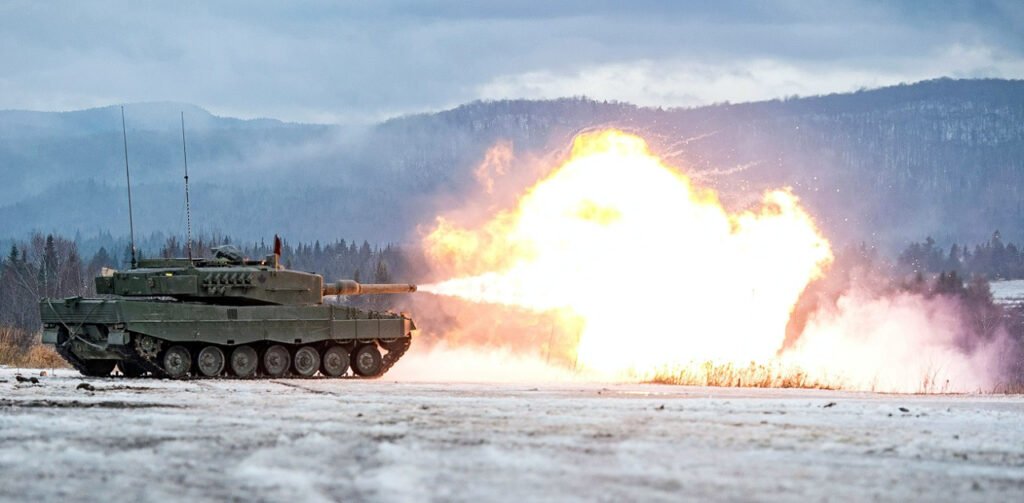
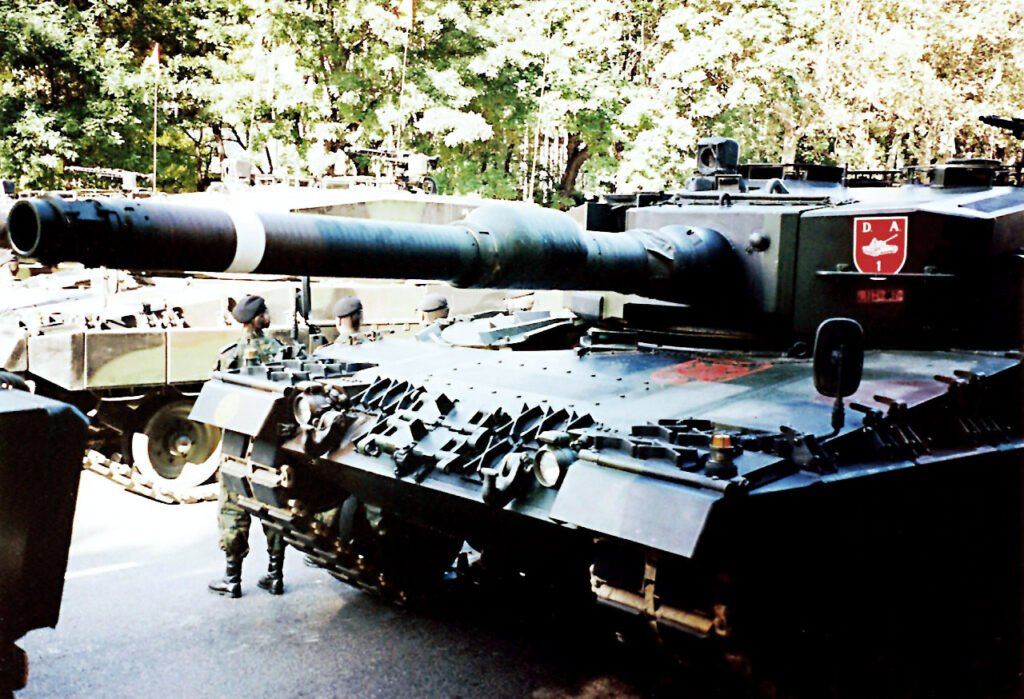
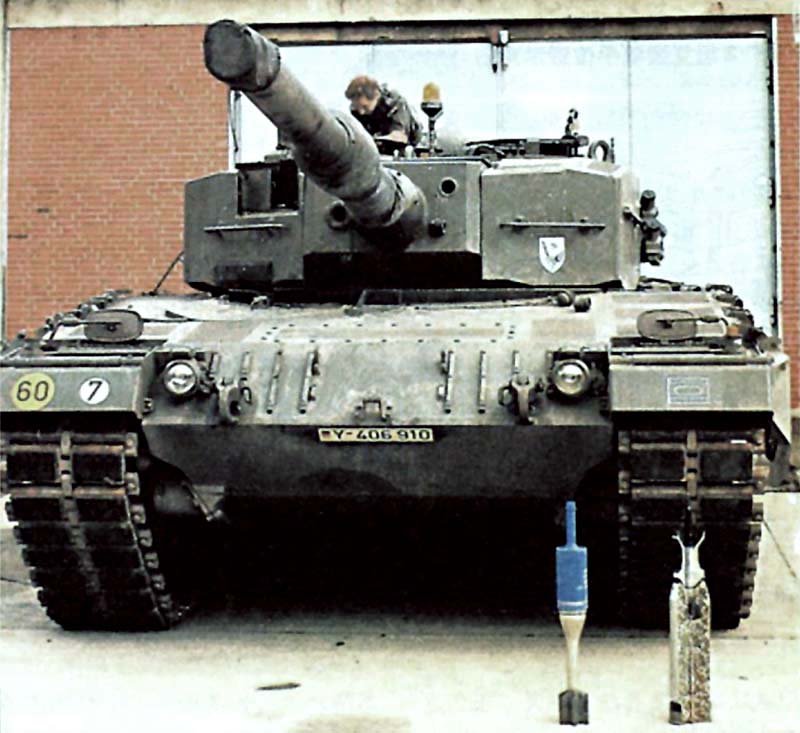
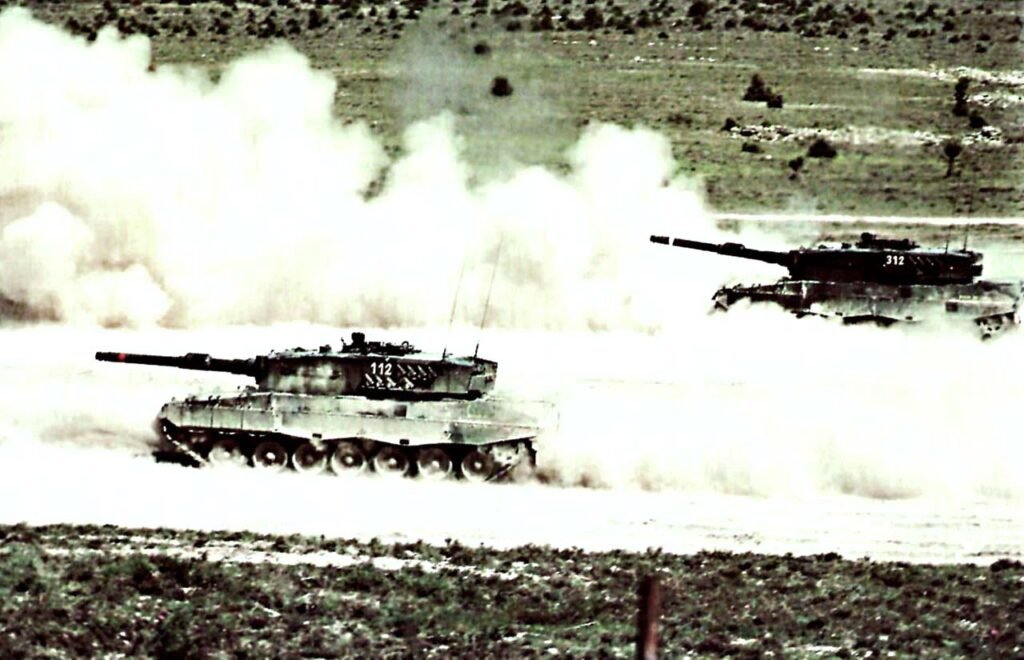
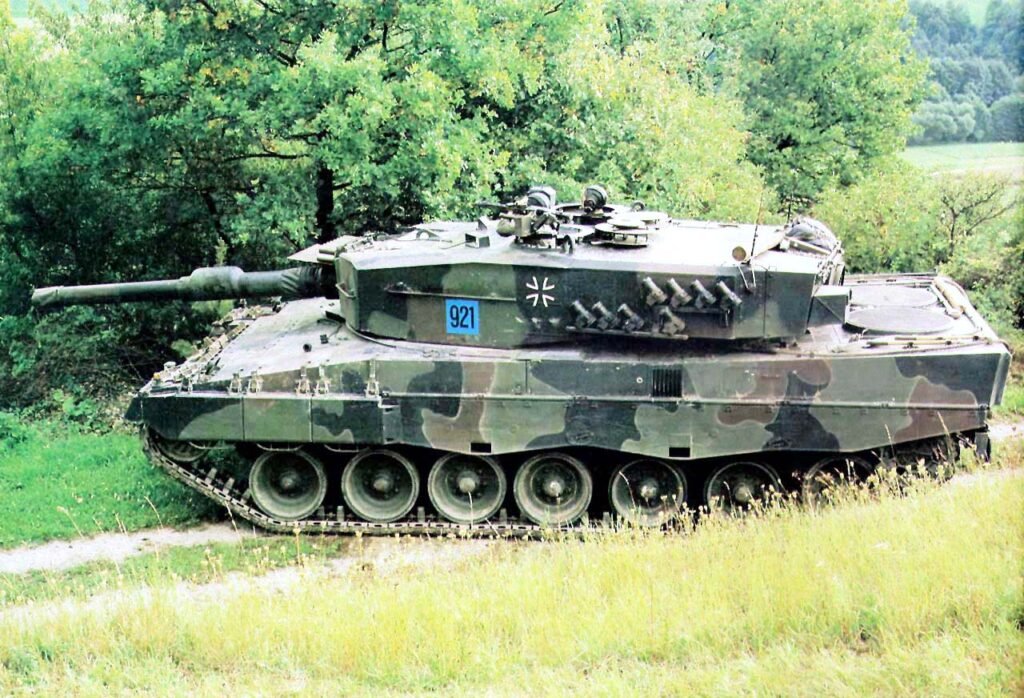
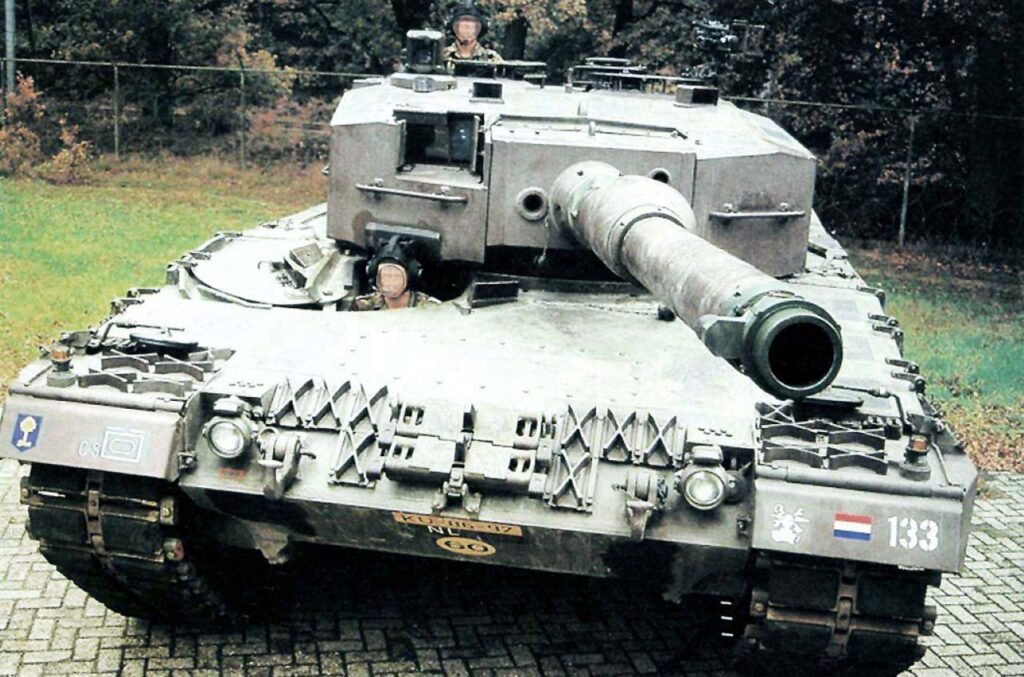
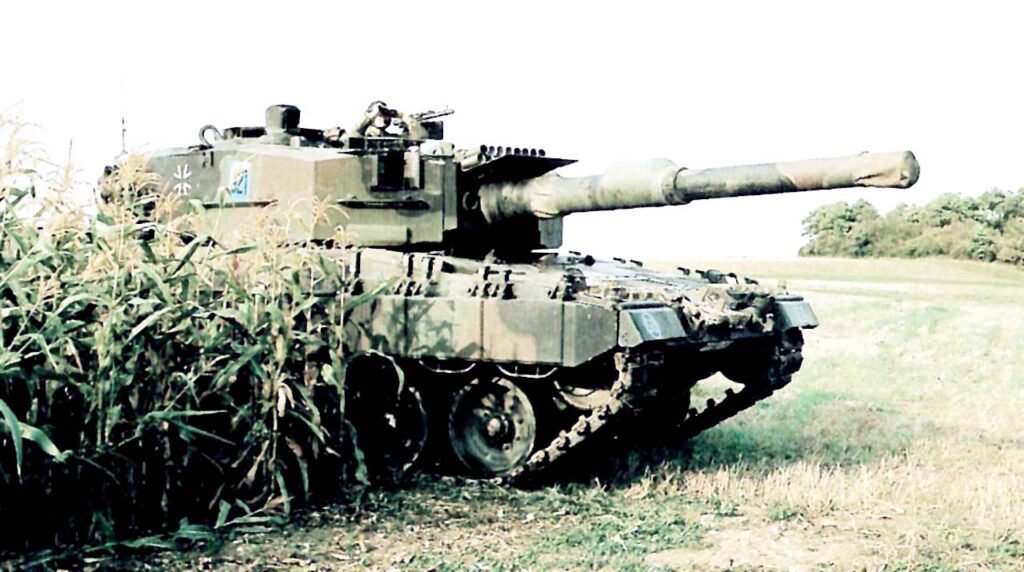
LEOPARD 2 (A1-A4) MBT gallery 1
















































(Akv-151 prototype image). It all started in 1949 when the Kungliga Arméförvaltningen (KAF), (Royal Swedish Army Material Administration) requested a new...
(Ikv-91 prototype image). In the mid-60s the Swedish Army had a large fleet of armored combat vehicles that after many years...
(Brobv-941 prototype image). Despite previous attempts by the Swedish Army to have a dedicated armored bridgelayer, it can be said that...